Data model
This document is based on the wallet-frontend PR #740 description, lightly edited.
Introduction
This implementation leverages the Event Sourcing model for managing wallet session state. Instead of persisting every event indefinitely, this implementation maintains a WalletBaseState as the starting point and apply a sequence of WalletSessionEvents stored in memory. The current state is derived by reducing these events over the base state using the map-reduce pattern.
By reducing a sequence of session events over a known base state, this approach achieves fast state rehydration, which is critical for responsive in-memory operations. Additionally, the use of reducer functions enhances testability, allowing to verify state transitions in isolation with minimal overhead. The model is also extensible, as new event types or behaviors can be integrated by extending the reducer logic without altering the overall architecture.
Summary of introduced features
- State synchronization across devices
- Client-side encrypted storage for credentials, presentations, settings and state
Details
The wallet state consists of a WalletBaseState S,
and a list of events as illustrated by the following figure.
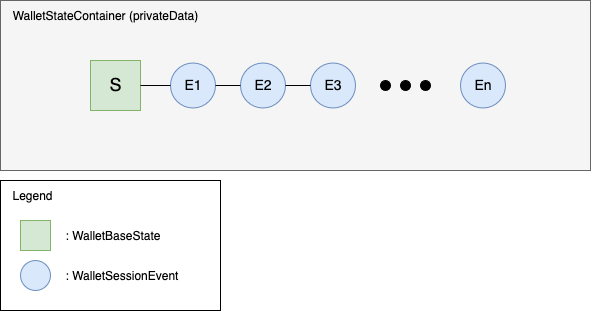
S: WalletBaseState
- keypairs
- credentials
- presentations
- settings
- credential issuance session states
events: List<WalletSessionEvent> (E1, E2, ..., En)
- Describes a change to S (
WalletBaseState) parentHash: hash of previous event- ...other metadata
Current state is S + E1 + E2 + ... + En, recomputed each time the encrypted container is opened (on each page load)
Events older then some threshold, get folded into the S (WalletBaseState)
S' = apply(S, events[0])
events = events[1:]
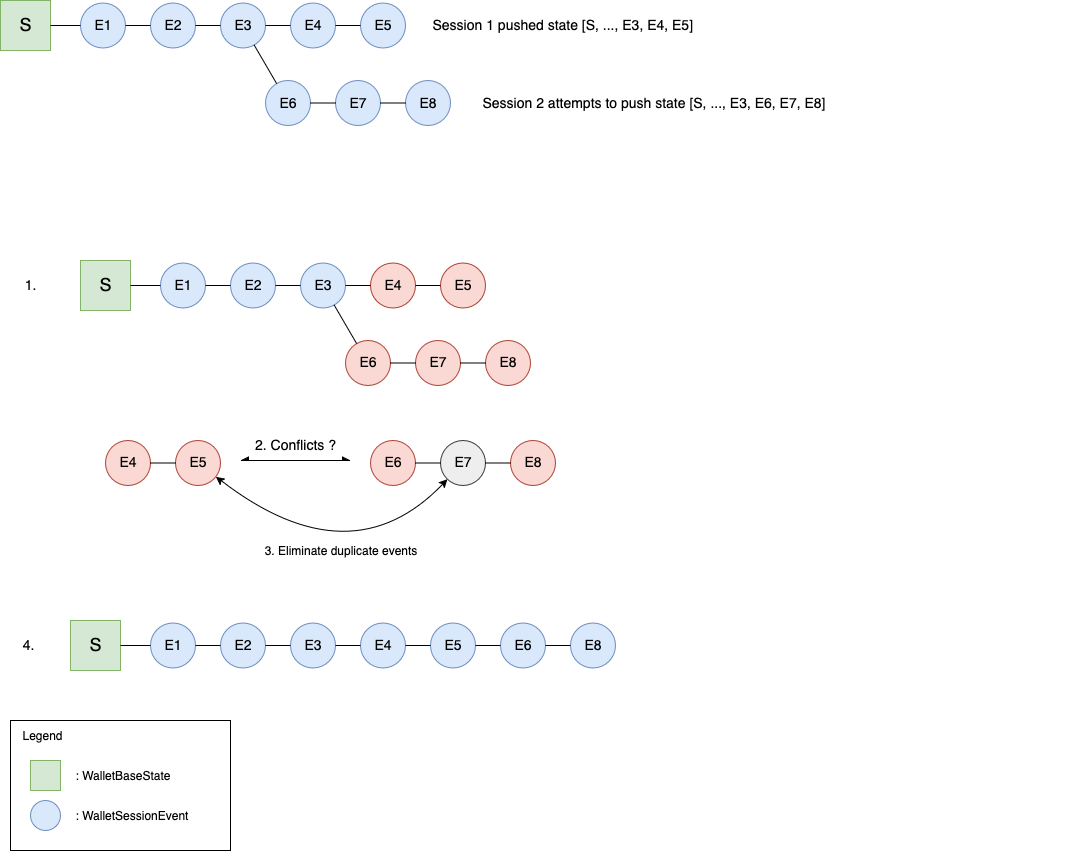
Conflict detection
Utilize ETag header for conflict detection
On fetch: save ETag header in frontend state
Backend sets response header
ETag: Hash(encrypted blob)Frontend saves
ETagin app statelatestEtag = response.headers['ETag']
On push: send request header X-Private-Data-ETag: <latestEtag>
- Backend compares:
Hash(currentPrivateData) == X-Private-Data-ETag - if match: success
- if not matched: conflict
- Frontend must re-fetch and resolve conflict (on later PR)
Conflict resolution
The above diagram provides an illustrative example. The resolution steps as numbered in the diagram are:
Use
parentHashto determine the point of divergenceIn the example case,
Hash(E3)is the latestparentHashthat appears in both event listsResolve conflicts between E4...E5 and E6...E8
- New Credential Event: keep both if
credentialIddiffer - Delete Credential Event: keep both if
credentialIddiffer. Discard if duplicatecredentialid - New Keypair Event: keep both
- Delete Keypair Event: Discard if duplicate
kid - Alter Settings Event: Keep the one with the latest timestamp
- New Credential Issuance Session: Keep both
- New Presentation Event: keep both
- New Credential Event: keep both if
De-duplicate events: E7 duplicates E5
After conflict resolution, replay E6, E8 after E5
Note: The implementation at this point did not handle the cases of offline scenarios where merging of divergent states can occur. This functionality will be introduced later.
Code versioning
This section is new since wallet-frontend PR #740.
The data model is implemented in WalletStateSchema.ts and related files.
Each version of the data model has a concrete versioned module, for example WalletStateSchemaVersion1.ts,
which defines data types and functions for operating on events for that schema version.
Concretely, these consist of:
Type definitions of
WalletStateContainer,WalletStateandWalletSessionEvent, and any required member types.WalletStateContaineris always on the form:export type WalletStateContainer = {
events: WalletSessionEvent[];
S: WalletState;
lastEventHash: string;
};In schema version 1,
WalletSessionEventandWalletStateare both concrete singular types. In later schema versions these are "version X or earlier" union types, sinceeventsmay contain events of earlier schema versions not yet folded intoS, and the last event folded intoSmay also have been of an earlier schema version. Therefore, bothSandeventsmay be of the current or any earlier schema version.Reducer functions for applying events to states. These functions have signatures on the form
(S, E) => S, whereSis the state type andEis the event type.The
(WalletState, WalletSessionEvent) => WalletStatereducer should always setWalletState.schemaVersionto the value ofWalletSessionEvent.schemaVersion.Merge strategies for de-duplicating events during conflict resolution. These are functions that take two lists of events of a particular type, and return a new list that is the de-duplication result.
A hash function for hashing events. This is used to set the
parentHashof child events, and thelatestEventHashof theWalletStateContainer.Utility functions for initializing a new wallet state, and moving events to new parents during conflict resolution.
Whenever hashing an event, or applying an event to a state,
the function suite defined in that event's schema version must be used.
These WalletStateSchemaVersionX.ts files therefore cannot be deleted or edited
(except pure refactorizations) without breaking backwards compatibility.
Subsequent versions can reuse code from previous versions by importing their types and functions, and re-exporting them from the new module with any necessary extensions. Inherited functions can be "modified" by wrapping the existing function with any necessary adapter logic, or "overwritten" by re-exporting a new function of the same name.
To ease code reuse between schema versions,
part of the WalletStateSchemaVersion1 function suite is constructed using a createOperations factory function.
This way the event reducer, hash function and merge strategies
can be easily adapted to accept events from a later schema version
if the relevant logic did not change between those schema versions.
Functions for creating events are in WalletStateSchema.ts,
and always target the most recent schema version.
This ensures that the schema version of the state and event log is a non-decreasing sequence.